![]() Updated: 12/1/96
Updated: 12/1/96
![]() Updated: 12/1/96
Updated: 12/1/96
To understand the virus/cancer link it is necessary to
examine a bacterial/phage relationship that initially put us on the trail
of how viruses produce cancers in humans. Remember how E. coli
became the most studied bacterium on the planet? Well it turns out that,
like most (maybe all) bacteria, E. coli has lots of phage that munch
on it and, not surprisingly, these E. coli phage were intensely
studied along with the bacterium. One group of E. coli phage (T-even)
were found to always result in the death of the infected cell after about
30 minutes. These phage came to be called LYTIC PHAGE as they always fatally
lysed the E. coli host. These lytic phage produce the CLEAR
PLAQUES that you see in the lab.
However, another group of E. coli phage were found that didn't always
result in the immediate lysis and death of the host. Rather, it was noted
that these phage "DISAPPEAR" following infection, only to reappear many
bacterial generations later. Eventually it was discovered that the DNA
of these viruses could INTEGRATE into
the E. coli DNA, effectively becoming a "hitchhiker" on the E.
coli genome. That is the ENTIRE VIRAL GENOME could FUSE
into the E. coli genome and be REPLICATED
ALONG WITH IT over many generations. In this state the virus
become LATENT, which means that there
is no easy way to tell that it is even there. To the early investigators
it seemed like the virus had DISAPPEARED
as if by magic. As described below eukaryotic viruses also do this (Fig.
1).
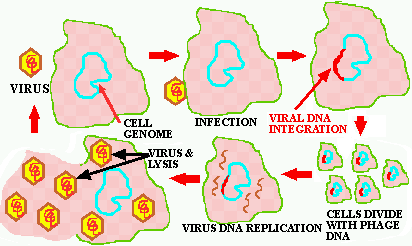
Figure 1. General depiction of temperate virus life cycle. The infected cell could be a bacterial or eucaryotic host.
![]() PROPHAGE
or PROVIRUS = the term "prophage" refers
to a phage genome that has been integrated into the host's DNA, whereas
the term "provirus" is the more general term and refers to any viral genome
that becomes incorporated or integrated in a host genome. A prophage is
a provirus, but not all proviruses are prophage.
PROPHAGE
or PROVIRUS = the term "prophage" refers
to a phage genome that has been integrated into the host's DNA, whereas
the term "provirus" is the more general term and refers to any viral genome
that becomes incorporated or integrated in a host genome. A prophage is
a provirus, but not all proviruses are prophage.
![]() LYSOGENIC
cell or LYSOGEN = a bacterial host
that has a prophage integrated into its genome. This refers to a host that
has been "lysogenized" by a temperate phage's genome integrating into its
genome.
LYSOGENIC
cell or LYSOGEN = a bacterial host
that has a prophage integrated into its genome. This refers to a host that
has been "lysogenized" by a temperate phage's genome integrating into its
genome.
FAQ: "If temperate phage integrate and disappear, how can we even see them and how were they found in the first place?"
ANSWER: It turns out that when a bacterial host is infected with a TEMPERATE phage, a RACE ensues between integration and new phage formation. The latter results in lysis and death of the host cell, whereas in the former case the cell survives, the virus enters the latent, or prophage phase, and the cell continues to replicate normally. Since lysis wins about 50% of the time, the plaques that are formed are TURBID or CLOUDY due to the growth of MICRO COLONIES of LYSOGENS. Cells isolated from these colonies turn out to contain PROPHAGE and to be immune from infection by the original phage.
The term PROPHAGE or PROVIRUS comes from the observation
that under certain conditions, the lytic cycle of the phage can be ACTIVATED
to go into the lytic cycle, which results in phage replication & host
death. So in EVERY CULTURE of a lysogen, one FINDS SOME PHAGE that have
resulted from the SPONTANEOUS activation
of the prophage in a few cells. Thus the virus maintains itself in two
forms, which you must admit is a neat, if devious, trick (the little
devils). We have learned how to activate some prophage. For example,
the lambda phage, which is one of the most studied phage (![]() because, naturally in grows in E. coli), is activated by
a brief exposure to UV-light. So one can expose a lysogenic culture to
UV and 20 minutes later all the cells LYSE and the medium
clears.
because, naturally in grows in E. coli), is activated by
a brief exposure to UV-light. So one can expose a lysogenic culture to
UV and 20 minutes later all the cells LYSE and the medium
clears.
It turns out that the PROVIRUS ISN'T really INERT, but it often contributes FUNCTIONAL GENES to the lysogen that can CHANGE its PHENOTYPE. This is called LYSOGENIC CONVERSION. For example, the prophage can result in a change in virulence as it does in the case of Clostridium botulinum and the diphtheria bacterium. In both cases, the host bacterium is AVIRULENT (not a pathogen) until it integrates a certain prophage (different phage for each bacterium of course). In other cases the prophage results in a change of the antigenicity of the host cell so that it responds to DIFFERENT ANTIBODIES. It appears that temperate phage are yet another way nature has devised of testing out the efficacy of mixes of various genes in the survival game.
![]() OK! this is all very interesting and I'm sure it turns on loads of scientific
types, but what does it have to do with CANCER? Do temperate phage cause
cancer or something? Fortunately, temperate phage only bedevil bacteria,
but we have a whole host of similar viruses that do appalling things to
us in their blind, pitiless desire to survive.
OK! this is all very interesting and I'm sure it turns on loads of scientific
types, but what does it have to do with CANCER? Do temperate phage cause
cancer or something? Fortunately, temperate phage only bedevil bacteria,
but we have a whole host of similar viruses that do appalling things to
us in their blind, pitiless desire to survive.
![]() NEOPLASM
or TUMOR = an abnormal and UNREGULATED
growth of cells.
NEOPLASM
or TUMOR = an abnormal and UNREGULATED
growth of cells.
![]() BENIGN
TUMOR = a tumor that STAYS where it
started.
BENIGN
TUMOR = a tumor that STAYS where it
started.
![]() MALIGNANT
TUMOR = a tumor that throws off cells
that MIGRATE to other parts of the
body where they grow uncontrollably.
MALIGNANT
TUMOR = a tumor that throws off cells
that MIGRATE to other parts of the
body where they grow uncontrollably.
![]() METASTASIS
= the SPREADING PROCESS of a malignant
tumor. A malignant tumor that has spread to other parts of the body is
said to have METASTASIZED.
METASTASIS
= the SPREADING PROCESS of a malignant
tumor. A malignant tumor that has spread to other parts of the body is
said to have METASTASIZED.
![]() TRANSFORMED
CELL = a cell that no longer responds
to signals that limit its growth. Transformed cells grow in multiple layers
on a solid surface whereas normal cells grow as a monolayer on a solid
surface.
TRANSFORMED
CELL = a cell that no longer responds
to signals that limit its growth. Transformed cells grow in multiple layers
on a solid surface whereas normal cells grow as a monolayer on a solid
surface.
![]() ONCOGENE
= a gene that CAUSES cancer.
ONCOGENE
= a gene that CAUSES cancer.
![]() ONCOLOGY
= is the study of cancer by ONCOLOGISTS.
ONCOLOGY
= is the study of cancer by ONCOLOGISTS.
Although many cancers can not be cured and we're far from
explaining the entire cancer scenario, we have made significant progress
in understanding & treating many cancers. We know that there are MANY
CAUSES OF CANCER. These include genetic defects, carcinogens
(chemical
and radiation), viruses, and repeated injury to tissue. On Feb. 23, 1996
the discovery of a gene that appears to be responsible for many types of
cancers was reported. The significance of this discovery, if validated,
appears very promising. We know that some cancers are ENVIRONMENTALLY
PRODUCED and thus, to a significant degree, PREVENTABLE. The
exact number or percentages of environmentally induced cancers causes a
lot of HOT AIR to be blown about which serves mainly to cloud the real
issues. Since much ENVIRONMENTALLY-BASED
cancer induction is tied closely to physical pleasures (food, sex, drugs
etc.), it is easy to disregard the facts and to feed off MYTHS
that allow us to justify doing what we want to do. For example, there is
OVERWHELMING
DATA showing that the major cause of LUNG CANCER is (are you
sitting down for this?) smoking (would I kid you?); that
ALCOHOL CONSUMPTION significantly increases
one's chances of getting liver, intestinal and esophageal cancer; that
excessive FAT consumption increases
the chances of getting breast and other cancers; that exposure to sunlight
increases the changes of getting the most common form of cancers, those
effecting the skin. Further, there is recent scientific data proving
that the sun comes up in the EAST, at least on most days![]() .
.
There is also much data showing that even when people accept these facts to be true, they persist in risky behavior. I think it is important to ask why?
The physiological and psychological nature of the cancer situation is more EASILY UNDERSTOOD by recognizing the following FACTS:
![]() Cancer is, in the vast majority of cases, a MULTISTEP
PROCESS .
Cancer is, in the vast majority of cases, a MULTISTEP
PROCESS .
![]() Cancer is commonly a condition mainly of AGE.
Cancer is commonly a condition mainly of AGE.
The MULTISTEP nature of cancer means that clinical cancer is the FINAL STAGE that involves a series of cellular changes that are not always seen as even REMOTELY RELATED. Each of these changes produces an INTERMEDIATE STAGE and the process can STOP at any stage or progress very rapidly under certain conditions. Oncologists are beginning to unravel these various stages. We now know that cells contain genes that CONTROL CELL GROWTH in a number of ways. In healthy cells these genes are called PROTO-ONCOGENES. Proto-oncogenes REGULATE GROWTH by telling the cell when to stop growing and when to grow. However, if these genes mutate or if they are moved to the wrong place in the chromosome (a type of mutation) they can result in cancer. When this happens they become ONCOGENES.
Therefore the cause and effect of actions that contribute to cancer are usually SEPARATED BY TIME AND CIRCUMSTANCE. For example, a person who smokes usually does not suffer from lung cancer until they are past 40. They may regret having smoked, but the damage has accumulated step by step, slowly, over such a long period that no effective connection is visible until too late. One of the characteristics of humans that contributes to this problem is the feeling of INVULNERABILITY, particularly when young. This and the tendency of humans to GAMBLE even when they know the odds are against them, often makes for a lethal combination in the case of cancer (don't even mention me & chocolate!).
![]() The
human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 or HTLV-1 that produces leukemia
The
human T-cell lymphotropic virus-1 or HTLV-1 that produces leukemia
![]() Several
herpes viruses, including the Epstein-Barr virus.
Several
herpes viruses, including the Epstein-Barr virus.
![]() Hepatitis
B virus
Hepatitis
B virus
![]() Papilloma
virus.
Papilloma
virus.

Figure 2. Multistep process of cancer formation. This is a likely scenario of the series of steps leading to cancer formation. A set of four healthy genes are seen at the top. The first mutation, in the gray gene on the left, results in somewhat more mRNA being produced than normal. A second mutation, some years later occurs in the green gene on the right which produces slightly less mRNA than it normally should. These two mutations may result is an ALTERED CELL TYPE that grows a bit strange but is not cancerous at this stage. Finally, a 3rd mutation occurs in the red gene which results in that gene being turned on at the wrong time. The combination of these 3 mutations finally produces a cancer with the ability to metastasize to other sites. The entire process may take 3 or 50 years or stop at any stage.
However, the nature of this relationship is not always clear. For example, women suffering from genital herpes have a higher frequency of cervical cancer, yet it is not clear if it is always the herpes virus that directly induces the cancer or if it is a case of repeated insult (damage) to the tissue that leads to the cancers. One problem is that there is evidence that DNA viruses that infect a cell may DISAPPEAR, after inducing genetic rearrangement of proto-oncogenes that are a step in the sequence leading to cancer or they may have left behind oncogenes. This situation is roughly similar to that of LYSOGENIC CONVERSION described above. Viruses, in general weaken the immune response and it may be that this allows cancers that normally would be destroyed by our own immune system to escape detection long enough to become established.
With RNA viruses the situation is even more complex. This is not the course for going into the complexities of RNA replication, so I am going to present some GENERALITIES and only discuss one RNA virus in detail.
THE GENERAL POINTS:
![]() RNA viruses can replicate in several different ways, depending on the virus.
RNA viruses can replicate in several different ways, depending on the virus.
![]() Some RNA viruses pass through an INTERMEDIATE DNA stage and other do not.
Some RNA viruses pass through an INTERMEDIATE DNA stage and other do not.
![]() Some RNA viruses can act as their OWN mRNA, while other can't.
Some RNA viruses can act as their OWN mRNA, while other can't.
Important RNA viruses include: the polio viruses (ask your parents & grand parents about life before the polio vaccine), many of the common cold viruses, rabies virus, and the HIV virus.
The important DNA viruses that effect humans include the herpes viruses, the pox viruses, the adenoviruses and the papovaviruses. Again the details of their replication is not a suitable topic of this course.
The viral DNA now becomes a PROVIRUS that transcribes
viral mRNA from which new viruses are produced. Retroviruses were the first
viruses to be shown to produce cancer in humans and they are the etiological
agent of AIDS, about which you will learn more in Chapter
17. Reverse transcriptase is now one of the major tools of genetic
engineering because it allows the copying of mRNA into DNA. What this means
is that if you have a gene that is actively being transcribed
(and
producing truck loads of mRNA), from a gene you desire to isolate, you
have only to collect this mRNA, mix it with reverse transcriptase and VIOLA!!,
you have one DNA strand of the GENE YOU FANCY. You can now convert it to
a double stranded form with DNA polymerase (piece-of-cake!) which
gives you the COMPLETE DOUBLE STRANDED FORM which can now be cloned
etc.
and you can buy your ticket to Sweden to collect your very own Nobel Prize--at
this point most of us wake up and wipe away the tears when we realize it
was all a dream. But it could happen!
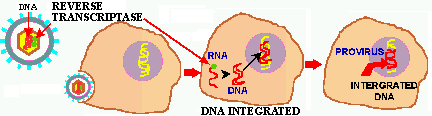
Figure 3. Retrovirus infection. The reverse transcriptase directs the synthesis of a strand of DNA from the RNA genome. This is converted into double stranded DNA which subsequently migrates into the nucleus and is integrated into the host's genome.
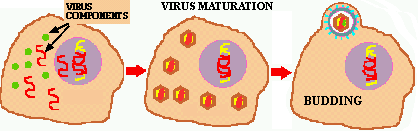
Figure 4. Retrovirus replication. Once the viral DNA is incorporated into the host's DNA it can transcribe mRNA from which the various enzymes and structural components of the virus are translated. These are them assembled into complete virions which bud out of the cell.
![]() All viruses are a nucleic acid polymer of either RNA or DNA, BUT
NEVER BOTH, covered with a protein coat.
All viruses are a nucleic acid polymer of either RNA or DNA, BUT
NEVER BOTH, covered with a protein coat.
![]() Viruses are rather specific as to the hosts and host's cells they will
attack because of the specificity of the DOCKING
PROTEINS.
Viruses are rather specific as to the hosts and host's cells they will
attack because of the specificity of the DOCKING
PROTEINS.
![]() Viruses, although simple in composition, when compared to eu- and prokaryotes,
are never-the-less so complex that
we still haven't figured out how they work.
Viruses, although simple in composition, when compared to eu- and prokaryotes,
are never-the-less so complex that
we still haven't figured out how they work.
![]() No viral disease has ever been CURED
by outside intervention. A host either cures the virus, or controls it,
or dies.
No viral disease has ever been CURED
by outside intervention. A host either cures the virus, or controls it,
or dies.
![]() Viral disease represent one of the most dangerous challenges to mankind
that exist.
Viral disease represent one of the most dangerous challenges to mankind
that exist.
SCIENCE HALL, ROOM 440CA
PHONE: 509-335-5108
FAX: 509-335-1907
E-MAIL: hurlbert@mail.wsu.edu or hurlbert@wsu.edu hurlbert@pullman.com
OFFICE HOURS: M,W 1:30 to 3:30 PM.
Return to Table of Contents